What Are the Different Types of Ibuprofen and What Are They Used For?
What Are the Different Types of Ibuprofen and What Are They Used For?
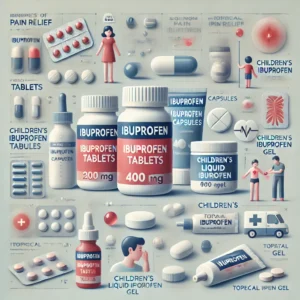
Ibuprofen is one of the most commonly used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and it is widely used for pain relief, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever. There are many forms of ibuprofen available on the market, including tablets, capsules, syrups, and gels, each varying in concentration, formulation, and appearance.
How Does Ibuprofen Work?
Ibuprofen works by blocking enzymes called cyclooxygenases (COX), which play a key role in the production of prostaglandins, chemicals that contribute to pain, fever, and inflammation. By blocking these enzymes, ibuprofen helps reduce these symptoms, making it a go-to medication for a wide variety of painful and inflammatory conditions.
Types of Ibuprofen
There are various types of ibuprofen on the market, differing not only in concentration but also in additional ingredients and methods of administration. Here are some common types:
- Ibuprofen 200 mg: This is the most common over-the-counter dose, available without a prescription. It is used to relieve mild to moderate pain, such as headaches, muscle aches, menstrual pain, and fever.
- Ibuprofen 400 mg and 600 mg: These higher doses of ibuprofen are often available by prescription only. They are used to treat more severe pain, such as joint pain from arthritis or post-surgery discomfort.
- Ibuprofen 800 mg: This is the highest dose of ibuprofen available by prescription. It is typically used for chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or severe pain.
- Ibuprofen Gel: Ibuprofen is also available in topical gel or cream form, which is applied directly to the skin to relieve localized pain and inflammation, such as muscle strains or joint pain.
- Children’s Ibuprofen: For children, ibuprofen is available in lower doses, usually in syrup or chewable tablet form, suitable for reducing fever or pain associated with colds, ear infections, or teething.
Ibuprofen 114 Pill (Red Ibuprofen)
One specific type of ibuprofen is the Ibuprofen 114 Pill, a red tablet imprinted with the number “114”. This form of ibuprofen contains 800 mg of the active ingredient and is commonly prescribed for treating more intense pain or chronic inflammation that cannot be managed by lower doses. This type of ibuprofen is often prescribed for conditions such as:
- Arthritis: For patients with rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, it helps reduce joint inflammation and alleviates pain.
- Chronic Pain: In cases of persistent or recurring pain, such as chronic back pain or post-injury rehabilitation.
- Post-Surgery Pain: Ibuprofen 800 mg is also frequently used after surgeries or injuries to help reduce pain and speed up recovery.
Maximum Dosage of Ibuprofen
It is important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines when taking ibuprofen to minimize the risk of side effects and complications.
- The maximum recommended dosage for adults for pain or fever relief is 1,200 mg per day, which equates to, for example, three 400 mg tablets if taking ibuprofen over the counter.
- For prescription use, the dosage may be increased to 3,200 mg per day, which means four doses of 800 mg. This dosage is used in cases of severe pain but must always be under medical supervision.
Dangerous Dosages of Ibuprofen
Taking more than the recommended maximum dose of ibuprofen can be extremely dangerous. Exceeding the recommended amounts can lead to serious health issues, including:
- Stomach Ulcers and Bleeding: Ibuprofen can irritate the stomach lining, leading to ulcers and, in some cases, life-threatening bleeding.
- Kidney Damage: Excessive use of ibuprofen can damage the kidneys, especially when taken long-term or in high doses.
- Cardiovascular Risks: Taking high doses of ibuprofen increases the risk of heart attack or stroke, particularly in patients with pre-existing heart conditions.
Taking more than 3,200 mg per day is considered dangerous and can result in severe complications, such as kidney or gastrointestinal damage.
In cases of extreme overdose, such as ingesting 6,000 mg or more at once, symptoms such as dizziness, vomiting, abdominal pain, breathing difficulties, or even organ failure may occur. If an overdose is suspected, immediate medical attention is required.
What to Watch Out for When Taking Ibuprofen?
 Even at recommended doses, it is important to be cautious, especially if taking ibuprofen for a long time. Side effects such as stomach issues, liver or kidney damage can occur if the dosage is not properly adhered to. Special care is needed if you are taking other medications that may interact with ibuprofen or if you have chronic health conditions.
Even at recommended doses, it is important to be cautious, especially if taking ibuprofen for a long time. Side effects such as stomach issues, liver or kidney damage can occur if the dosage is not properly adhered to. Special care is needed if you are taking other medications that may interact with ibuprofen or if you have chronic health conditions.
Conclusion
Ibuprofen is an effective medication for pain relief and inflammation reduction, but it’s important to use it wisely and follow the guidance of your doctor or pharmacist. Whether you are taking standard 200 mg ibuprofen or stronger variants such as Ibuprofen 114 Pill (800 mg), always ensure that you don’t exceed the recommended dose and monitor for any potential side effects. If you have any questions about using ibuprofen correctly, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare professional who can provide the best treatment advice based on your individual needs.